X 2 4 X 1
wikiborn
Sep 23, 2025 · 6 min read
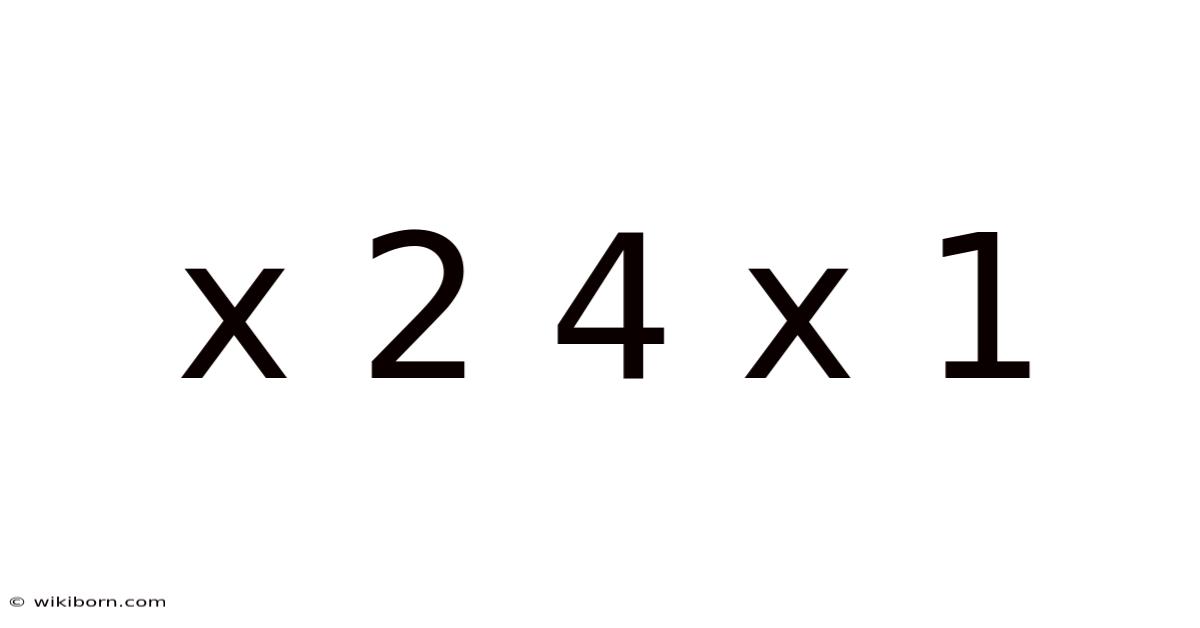
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: A Deep Dive into the Expression "x² + 4x + 1"
This article explores the mathematical expression x² + 4x + 1, examining its properties, applications, and methods for solving related equations. We'll unpack its significance in algebra, delve into its graphical representation, and discuss various techniques for finding its roots, offering a comprehensive understanding suitable for students and enthusiasts alike. Understanding this seemingly simple quadratic equation opens doors to broader mathematical concepts and problem-solving strategies.
Understanding Quadratic Equations
Before we dive into the specifics of x² + 4x + 1, let's establish a foundational understanding of quadratic equations. A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the second degree, meaning the highest power of the variable (in this case, x) is 2. The general form of a quadratic equation is ax² + bx + c = 0, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero. Our expression, x² + 4x + 1, is a quadratic expression; it becomes a quadratic equation when set equal to zero: x² + 4x + 1 = 0.
This seemingly simple equation holds a surprising depth. Its solutions, known as roots or zeros, represent the x-values where the equation equals zero. These roots are crucial in various applications, from physics and engineering to finance and computer science.
Methods for Solving x² + 4x + 1 = 0
Several methods can be used to find the roots of x² + 4x + 1 = 0. Let's explore the most common ones:
1. Factoring
Factoring involves expressing the quadratic equation as a product of two linear expressions. Unfortunately, x² + 4x + 1 doesn't factor neatly using integers. While some quadratic equations yield readily to factoring, this method isn't always applicable.
2. Completing the Square
Completing the square is a powerful technique for solving quadratic equations. It involves manipulating the equation to create a perfect square trinomial. Let's walk through the process:
- Move the constant term to the right side: x² + 4x = -1
- Take half of the coefficient of x (which is 4), square it (4), and add it to both sides: x² + 4x + 4 = -1 + 4
- Simplify: (x + 2)² = 3
- Take the square root of both sides: x + 2 = ±√3
- Solve for x: x = -2 ± √3
Therefore, the roots of the equation are x = -2 + √3 and x = -2 - √3.
3. Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula is a universal solution for finding the roots of any quadratic equation. It's derived from completing the square and provides a direct formula to calculate the roots. The formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
For our equation (x² + 4x + 1 = 0), a = 1, b = 4, and c = 1. Substituting these values into the quadratic formula yields:
x = [-4 ± √(4² - 4 * 1 * 1)] / (2 * 1) x = [-4 ± √(16 - 4)] / 2 x = [-4 ± √12] / 2 x = [-4 ± 2√3] / 2 x = -2 ± √3
This confirms the roots we found using completing the square.
Graphical Representation and the Discriminant
The graph of a quadratic equation is a parabola. The roots of the equation represent the x-intercepts of the parabola—the points where the parabola intersects the x-axis. The discriminant, represented by b² - 4ac, provides valuable information about the nature of the roots:
- b² - 4ac > 0: The equation has two distinct real roots. The parabola intersects the x-axis at two different points. This is the case with x² + 4x + 1 = 0.
- b² - 4ac = 0: The equation has one real root (a repeated root). The parabola touches the x-axis at a single point.
- b² - 4ac < 0: The equation has two complex roots (roots involving imaginary numbers). The parabola does not intersect the x-axis.
For x² + 4x + 1 = 0, the discriminant is 4² - 4(1)(1) = 12, which is greater than 0, indicating two distinct real roots. This is consistent with our findings using completing the square and the quadratic formula. Visualizing the parabola helps understand the significance of these roots.
Applications of Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations have widespread applications across various fields:
- Physics: Calculating projectile motion, determining the trajectory of objects under gravity.
- Engineering: Designing bridges, analyzing structural stability, optimizing shapes for minimal stress.
- Economics and Finance: Modeling economic growth, calculating investment returns, pricing options.
- Computer Science: Developing algorithms, creating simulations, solving optimization problems.
- Geometry: Finding areas and volumes of complex shapes, solving geometrical problems.
The seemingly simple equation x² + 4x + 1 = 0 is a fundamental building block in many of these applications. Understanding how to solve it unlocks the ability to address more complex problems within these domains.
Exploring Further: Variations and Extensions
Let's consider variations and extensions related to our core equation:
-
Inequalities: Instead of x² + 4x + 1 = 0, we might consider inequalities like x² + 4x + 1 > 0 or x² + 4x + 1 < 0. Solving these inequalities involves determining the intervals of x where the quadratic expression is positive or negative. This often involves analyzing the parabola's position relative to the x-axis.
-
Systems of Equations: We could have a system of equations involving x² + 4x + 1 and another equation. Solving such systems might involve substitution or elimination methods, leading to higher-order equations.
-
Complex Numbers: While our equation has real roots, understanding how to handle quadratic equations with complex roots is essential for broader mathematical proficiency.
-
Calculus: The derivative of x² + 4x + 1 is 2x + 4, which is used to find the minimum point of the parabola. The integral of x² + 4x + 1 is (1/3)x³ + 2x² + x + C, crucial for applications involving area calculations under the curve.
These extensions illustrate the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and the power of mastering fundamental equations like x² + 4x + 1 = 0.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is the 'a' in the quadratic formula not allowed to be zero?
A: If 'a' were zero, the equation would no longer be quadratic; it would become a linear equation (bx + c = 0). The quadratic formula is specifically designed for quadratic equations, where the highest power of the variable is 2.
Q: What does it mean if the discriminant is negative?
A: A negative discriminant indicates that the quadratic equation has no real roots. The roots are complex numbers, involving the imaginary unit 'i' (where i² = -1).
Q: Is there a way to solve x² + 4x + 1 = 0 without using the quadratic formula or completing the square?
A: While factoring doesn't work directly with integers, numerical methods like the Newton-Raphson method can approximate the roots to a high degree of accuracy. However, these methods are generally more computationally intensive.
Q: Can x² + 4x + 1 ever equal 0?
A: Yes! The equation x² + 4x + 1 = 0 has two real solutions (roots), which we calculated to be -2 + √3 and -2 - √3. These values, when substituted into the equation, will make it equal to zero.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple quadratic expression x² + 4x + 1, when set equal to zero, reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts and techniques. From the fundamental understanding of quadratic equations to the application of various solving methods like completing the square and the quadratic formula, and the interpretation of the graphical representation and the discriminant, this equation serves as a valuable stepping stone for more advanced mathematical studies. Its applications extend far beyond the classroom, impacting various fields of science, engineering, and finance. Mastering its nuances not only enhances mathematical skills but also builds a strong foundation for tackling more complex problems in the future. Remember, the journey of mathematical understanding is a continuous process of exploration and discovery; each solved equation opens new doors to further exploration.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 4 X 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.