What Is 2 X 2
wikiborn
Sep 23, 2025 · 6 min read
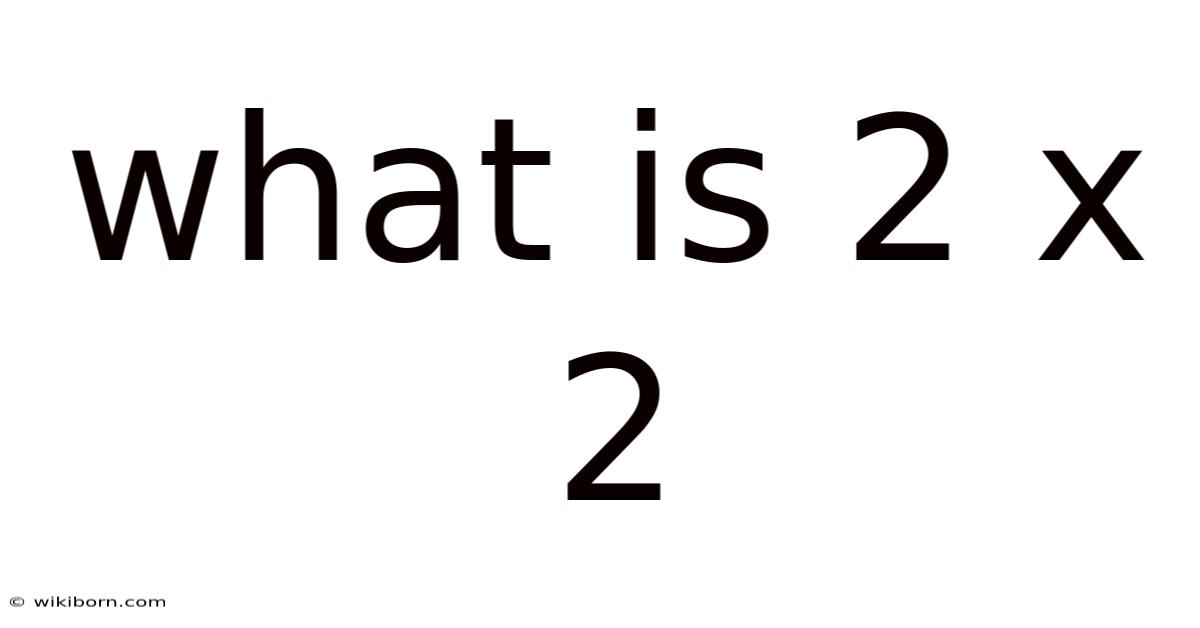
Table of Contents
What is 2 x 2? A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Implications
What is 2 x 2? This seemingly simple question, often encountered in early childhood education, opens a door to a vast world of mathematical concepts. While the answer, 4, is readily apparent to most, a deeper exploration reveals the fundamental principles of multiplication, its applications across various fields, and its significance in shaping our understanding of the world around us. This article will delve into the intricacies of this basic arithmetic operation, examining its historical context, practical applications, and abstract mathematical implications.
Introduction: The Foundation of Multiplication
Multiplication, at its core, is a form of repeated addition. 2 x 2 can be understood as adding two groups of two: 2 + 2 = 4. This simple representation forms the bedrock of understanding more complex multiplicative operations. It's the building block upon which more advanced mathematical concepts like algebra, calculus, and even abstract algebra are built. The seemingly trivial equation, 2 x 2 = 4, is a gateway to a universe of mathematical possibilities.
Understanding the Concept of "Times"
The multiplication symbol "x" signifies the process of repeating a number a specific number of times. In 2 x 2, "x" instructs us to take the number 2 and repeat it twice. This interpretation is crucial for understanding multiplication beyond basic arithmetic. It lays the foundation for understanding the concept of scaling, a crucial element in many scientific and engineering applications.
Visualizing 2 x 2: Practical Representations
Visualizing 2 x 2 can greatly enhance comprehension, particularly for younger learners. Several methods can be employed:
-
Arrays: Imagine a grid with two rows and two columns. By filling each cell, we see a total of four objects. This visual representation connects the abstract concept of multiplication to a tangible reality.
-
Groups of Objects: Picture two groups of two apples. Counting all the apples gives us a total of four. This method links multiplication to real-world scenarios, making the concept more relatable.
-
Number Lines: Starting at zero on a number line, take two jumps of two units each. This demonstrates the repeated addition aspect of multiplication.
Beyond the Basics: Extending the Concept
The seemingly simple 2 x 2 serves as a stepping stone to more complex multiplication problems. Understanding this fundamental operation allows for a smooth transition to multiplying larger numbers, decimals, fractions, and even negative numbers. The same underlying principle of repeated addition applies, albeit with slightly more complex calculations.
The Commutative Property: Order Doesn't Matter (in this case)
In the context of 2 x 2, the commutative property of multiplication becomes evident. This property states that the order of the numbers in a multiplication equation doesn't affect the result. 2 x 2 is equivalent to 2 x 2. While seemingly trivial here, this property holds significant importance in more advanced mathematical contexts.
Multiplication in Different Number Systems
The concept of 2 x 2 extends beyond the decimal system. The same principle applies to other number systems, such as binary (base-2) used extensively in computer science. In binary, 2 is represented as 10, and 2 x 2 would be calculated as 10 x 10 = 100 (which is equal to 4 in decimal). This demonstrates the universal applicability of multiplication principles across various numerical representations.
Applications of Multiplication: A World of Possibilities
The seemingly simple equation 2 x 2 has far-reaching applications in numerous fields:
-
Everyday Life: Calculating the total cost of two items priced at $2 each, determining the number of wheels on two bicycles, or dividing a group of four people into two pairs are all examples of everyday applications.
-
Engineering and Physics: Calculations involving area, volume, velocity, and acceleration often rely heavily on multiplication. For example, calculating the area of a square with sides of length 2 units uses 2 x 2.
-
Computer Science: Boolean algebra, fundamental to computer logic, utilizes multiplicative principles. Bitwise operations, crucial for data manipulation, frequently involve multiplying binary numbers.
-
Finance: Calculating compound interest, determining the total value of investments, and projecting future earnings all involve the application of multiplication.
-
Economics: Economic models rely on multiplicative relationships to analyze growth rates, production, and consumer behavior.
-
Chemistry: Stoichiometry, which governs the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions, extensively uses multiplication.
-
Statistics: Calculating probabilities, analyzing data sets, and conducting statistical inferences often utilize multiplicative operations.
The Abstract Mathematical Significance of 2 x 2
Beyond its practical applications, 2 x 2 holds significance in abstract mathematical concepts:
-
Group Theory: The concept of multiplication forms the basis of group theory, a branch of abstract algebra dealing with algebraic structures.
-
Ring Theory: Rings, another fundamental algebraic structure, involve operations that extend the concept of multiplication.
-
Field Theory: Fields are algebraic structures where both addition and multiplication are defined, demonstrating the interconnectedness of these fundamental arithmetic operations.
-
Linear Algebra: Matrices, which are arrays of numbers, utilize multiplication as a fundamental operation. Matrix multiplication finds wide application in computer graphics, image processing, and data analysis.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Despite its simplicity, some common misconceptions surround the concept of 2 x 2:
-
Confusion with Addition: Some individuals may mistakenly add the numbers instead of multiplying them. Visual aids and repeated practice can help clarify this distinction.
-
Difficulty with Larger Numbers: While understanding 2 x 2 is essential, transitioning to larger numbers may pose a challenge. Breaking down larger multiplication problems into smaller, more manageable steps can facilitate learning.
-
Misinterpretation of the Multiplication Symbol: The "x" symbol might cause confusion for some learners. Using alternative notations like "*" (asterisk) or parentheses can help clarify the operation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the difference between 2 + 2 and 2 x 2?
- A: 2 + 2 represents addition (combining two quantities), resulting in 4. 2 x 2 represents multiplication (repeated addition), also resulting in 4. While both yield the same result in this specific case, the underlying operations are distinct and have different applications in more complex contexts.
-
Q: Can 2 x 2 be represented in any other way?
- A: Yes, it can be represented as 2² (2 squared or 2 to the power of 2), which signifies 2 multiplied by itself. This introduces the concept of exponents and powers.
-
Q: Why is understanding 2 x 2 important?
- A: It forms the foundation for understanding more advanced mathematical concepts and has wide-ranging applications across various disciplines, from everyday life to complex scientific calculations.
-
Q: How can I help a child understand 2 x 2?
- A: Use visual aids like objects, arrays, or number lines to represent the concept of repeated addition. Relate it to real-world scenarios that the child can easily grasp.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of a Simple Equation
While the answer to "What is 2 x 2?" is simply 4, the journey to arrive at this answer and the exploration of its implications reveals a profound understanding of mathematical principles and their relevance in our lives. From its foundational role in basic arithmetic to its significant applications in various advanced fields, 2 x 2 serves as a powerful symbol of the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and their impact on the world around us. This seemingly simple equation is not just a calculation; it's a gateway to a world of mathematical understanding and innovation. The seemingly trivial holds within it the potential for significant growth and discovery. Mastering this basic operation lays the groundwork for tackling more complex mathematical challenges and fostering a deep appreciation for the beauty and power of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 2 X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.