3 2/3 As A Decimal
wikiborn
Sep 23, 2025 · 5 min read
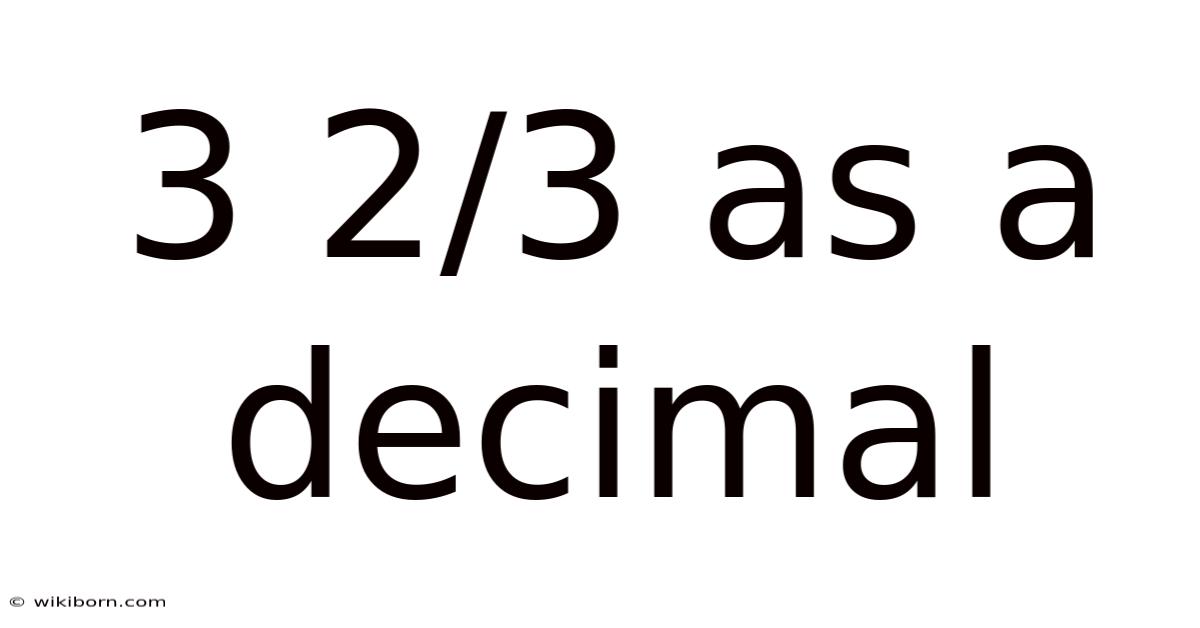
Table of Contents
Decoding 3 2/3 as a Decimal: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding how to convert fractions to decimals is a fundamental skill in mathematics, crucial for various applications from everyday calculations to advanced scientific computations. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of converting the mixed number 3 2/3 into its decimal equivalent, explaining the steps involved, exploring the underlying mathematical principles, and addressing common questions and misconceptions. We’ll also explore the practical applications of understanding this conversion. By the end of this article, you'll not only know the decimal equivalent of 3 2/3 but also have a solid grasp of the broader concept of fraction-to-decimal conversion.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Fractions
Before we begin the conversion, let's clarify the terminology. A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction, like 3 2/3. This represents 3 whole units plus two-thirds of another unit. The fraction itself, 2/3, consists of a numerator (the top number, 2) and a denominator (the bottom number, 3). The denominator indicates the number of equal parts a whole is divided into, while the numerator shows how many of those parts are being considered.
Converting 3 2/3 to an Improper Fraction
The first step in converting a mixed number to a decimal is to transform it into an improper fraction. An improper fraction has a numerator that is greater than or equal to its denominator. To do this, we multiply the whole number by the denominator and add the numerator. The result becomes the new numerator, while the denominator remains the same.
Here's how it works for 3 2/3:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 3 * 3 = 9
- Add the numerator: 9 + 2 = 11
- Keep the same denominator: 3
Therefore, 3 2/3 is equivalent to the improper fraction 11/3.
Converting the Improper Fraction to a Decimal
Now that we have the improper fraction 11/3, we can convert it to a decimal. The simplest method is to perform long division. We divide the numerator (11) by the denominator (3):
3.666...
3 | 11.000
-9
20
-18
20
-18
20
-18
2...
As you can see, the division results in a repeating decimal, 3.666... The digit 6 repeats infinitely. This is often represented as 3.6̅. The bar above the 6 indicates the repeating nature of the decimal.
Understanding Repeating Decimals
The appearance of a repeating decimal is a common occurrence when converting fractions to decimals, especially when the denominator of the fraction has prime factors other than 2 or 5. This is because our decimal system is based on powers of 10 (10 = 2 x 5), and if the denominator has prime factors other than 2 or 5, the division will not terminate cleanly.
In the case of 3 2/3, the denominator 3 is a prime number other than 2 or 5, leading to the repeating decimal 3.6̅.
Rounding Repeating Decimals
In practical applications, it's often necessary to round repeating decimals to a specific number of decimal places. For example, we might round 3.6̅ to:
- One decimal place: 3.7 (rounding up because the next digit is 6, which is greater than or equal to 5)
- Two decimal places: 3.67 (rounding up)
- Three decimal places: 3.667 (rounding up)
The level of precision required depends on the context of the problem.
Alternative Method: Using a Calculator
While long division provides a thorough understanding of the process, a calculator offers a quicker way to obtain the decimal equivalent. Simply enter 11 ÷ 3 into your calculator, and it will display the decimal representation, 3.666... or a similar notation for the repeating decimal.
Practical Applications of Decimal Conversion
The ability to convert fractions to decimals has numerous real-world applications:
- Measurements: Converting fractions of inches, meters, or other units to decimal form for more precise calculations.
- Finance: Calculating percentages, interest rates, and proportions involving fractions.
- Science: Expressing experimental results and performing calculations involving fractions.
- Engineering: Precise measurements and calculations in various engineering disciplines.
- Cooking and Baking: Following recipes accurately where ingredient quantities are expressed as fractions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is 3 2/3 a repeating decimal?
A: Because the denominator of the fraction (3) contains a prime factor (3) other than 2 or 5. When a fraction's denominator has prime factors other than 2 or 5, its decimal representation will be a repeating decimal.
Q: Can all fractions be converted to terminating decimals?
A: No. Only fractions whose denominators can be expressed as 2<sup>m</sup>5<sup>n</sup>, where 'm' and 'n' are non-negative integers, will result in terminating decimals.
Q: What is the difference between 3.666... and 3.6̅?
A: Both represent the same value, but 3.6̅ is a more concise way of representing the repeating decimal, indicating that the digit 6 repeats infinitely.
Q: How do I convert other mixed numbers to decimals?
A: Follow the same steps outlined above: convert the mixed number to an improper fraction, then divide the numerator by the denominator using long division or a calculator.
Conclusion
Converting the mixed number 3 2/3 to its decimal equivalent, 3.6̅, involves a straightforward process: transforming it into an improper fraction (11/3) and then performing long division or using a calculator. Understanding this process provides a strong foundation for working with fractions and decimals in various mathematical contexts. Remember that understanding repeating decimals and how to round them appropriately is crucial for practical applications. This knowledge isn't just for classroom exercises; it's a valuable tool for navigating numerous real-world situations requiring precise numerical calculations. Mastering this skill will enhance your mathematical abilities and equip you to handle a wide array of problems with confidence and accuracy.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3 2/3 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.